Different Type of Slabs & It’s Functionality.
What is a Slab?
A slab is generally a horizontal structural element of a building which is a thick layer of concrete reinforced with steel bars or any other composite materials. A slab is provided to have a flat surface like floor, deck and ceiling. The slab has a set of beams or walls to support it. These walls or beams are constructed with slab monolithically.
Type of Slabs:
Different type of slabs can be used based on varying loads coming over them and according to their functionality:
-
Conventional Solid Slab:
Conventional slabs are those slabs that have been used for a very long time and are commonly used. These slabs are supported with beams and columns where the depth of the beam is more than the slab. Slab functions to deliver its load to beams and then this load is transferred to columns to the foundation.
Conventional slabs are of two types:
If the ratio of longer span to shorter span is greater or equal to 2, then it is a One-way slab. If the ratio of longer span to shorter span is lesser or equal to 2, then it is a two-way slab.
-
One Way Slab:

The one-way slab is constructed by the cast-in-situ process. This slab is supported by beams on two opposite sides of the slab. One-way slabs are usually constructed where the span of the slab lies between 3-6 metres and live load varies between 3-5 KN/m2. The longer span is usually twice the shorter span. The main reinforcement is laid across the shorter span and distribution reinforcement is laid across a longer span.
-
Two Way Slab:

This slab is supported by beams on all four sides of the slab. Two-way slabs are usually constructed where the span of the slab lies between 6-9 metres and live load varies between 3-6 KN/m2. The shorter span is usually twice the longer span and all sides are subjected to bending. The main reinforcement is laid across both spans.
-
Joist/ Ribbed Slab (One-way joist slab):
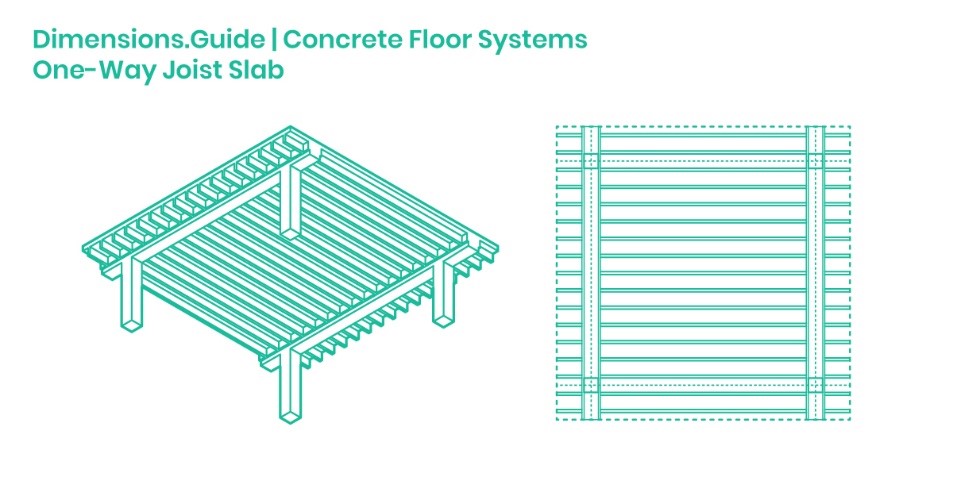
A joist slab or rib slab is supported by a number of ribs. These ribs support the slab to give extra strength in one direction. These slabs are economic, flexible and lighter in section. These joists are typically tapered and are spaced at uniform distances (not exceeding 750mm).
-
Waffle/ Grid Slab:
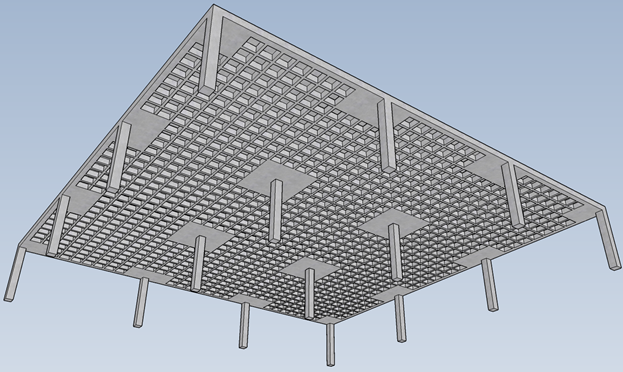
This type of slab is supported with square grids or waffles. This slab is preferred where span varies between 9-15 metres and live load of 4-7 KN/m2. This slab is constructed to increase strength for both spans.
-
Flat plates Slab:

These slabs can either be a one-way slab or a two-way slab which are supported directly on columns and walls. Thus, loads are directly transferred to columns. These slabs are suitable for spans varying between 6-8 metres. Flat plates require simple and cheap formworks.
-
Flat Slab:
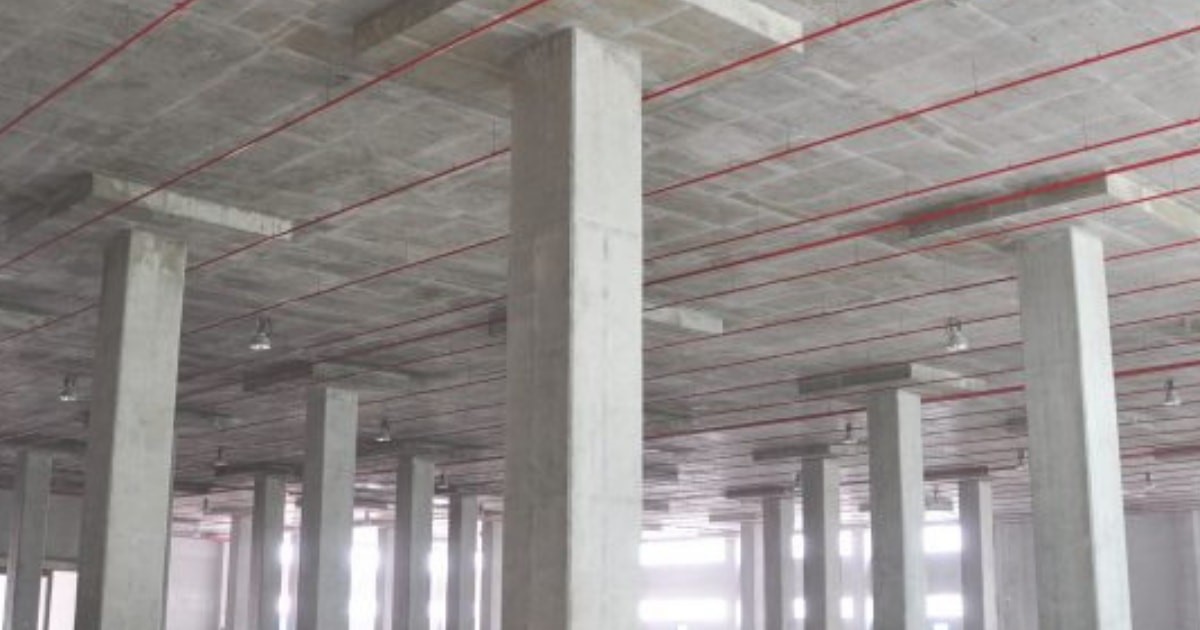

These slabs are supported directly on columns or caps. Thus, loads are directly transferred to columns. It can also be called a Beam-less slab. These slabs are suitable for spans varying between 6-9 metres. Flat slabs require a little complex but fewer formworks.
There are four types of constructing a flat slab:
- A Slab without drop and column without column head.
- Slab with drop and column without column head.
- the Slab without drop and column with column head.
- Slab with drop and column with column head.
-
Hollow Core Slab:

This slab is constructed with precast materials. These slabs reduce the self-weight of the structure while providing it strength. Their spans can vary largely but a width of 120 mm is standard and depth varies between 110mm to 400mm. Hollow core slabs have hollow spaces in their ribs which can be used as ducts.
-
Hardy Slab:
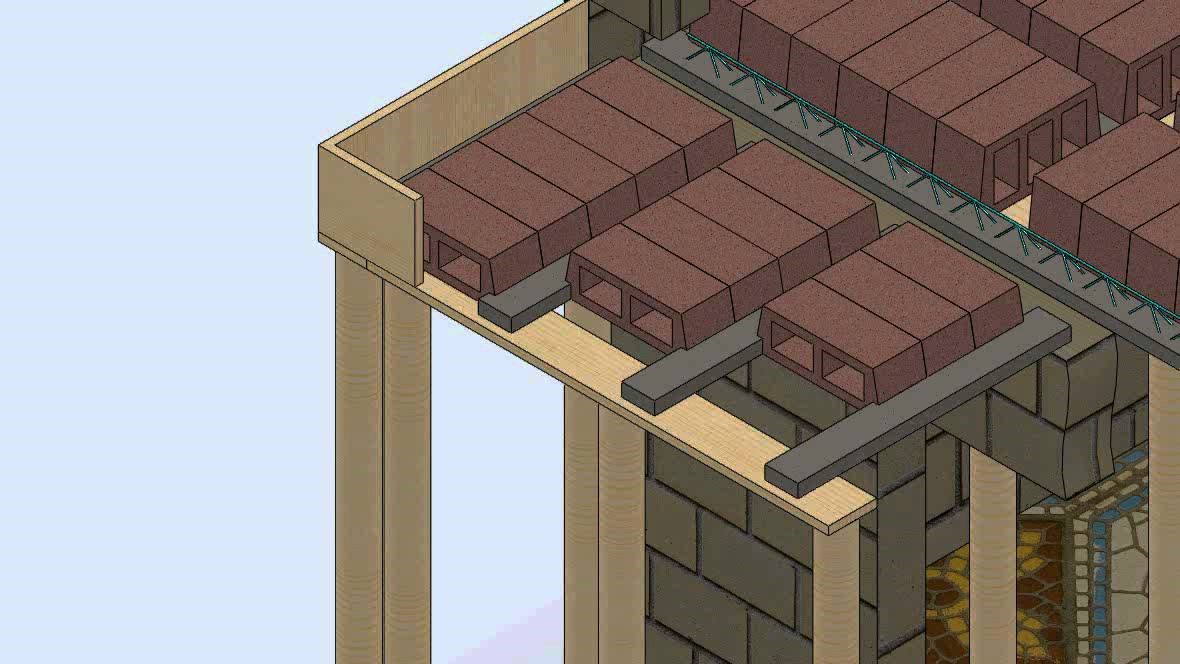
These slabs are constructed using hardy bricks which reduces the consumption of concrete in the slab and thus reduces the self-weight of the slab. It requires tedious formwork. It proves to economical for spans up to 5 metres. This slab is suitable for areas with high temperature because they are insulated with thermacol. The standard size of hardy brick is 40cm*20cm*20cm.
-
Bubble Deck Slab:

A bubble deck slab used prefabricated bubbles of plastic in the slab. Steel bars or reinforcing material is placed over and around these bubbles before pouring concrete. Bubble slabs reduce the self-weight of the slab while giving it strength.
-
Composite Slab:

This is a type of reinforced cement concrete slab which is laid over a steel mesh. This steel mesh serves to be a formwork and support for this slab.
-
Precast Slab:

These slabs are manufactured and cured in the factories and then brought to the site for final placing. Manufacturing it beforehand gives us efficiency and desired slab. The most common type of precast slabs is double T-type.
-
Dome Slab:
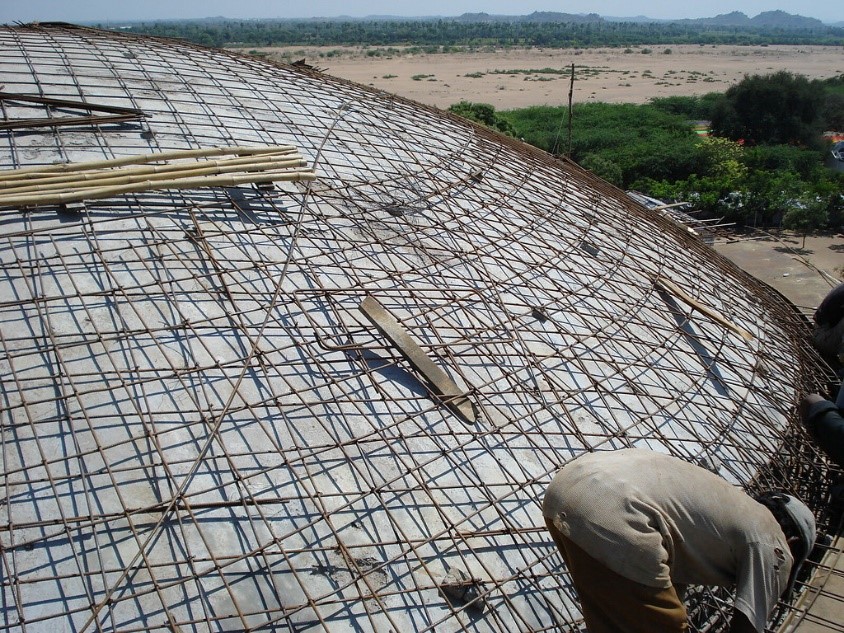

Dome slabs are best suited for temples, Mosques, palaces etc. to achieve a pleasant view of the structure. These slabs are usually hemispherical in shape. Most of the ancient structures have this slab where a Dome slab is constructed over a conventional slab to bear all the compressive forces. The Dome slab is generally 0.15 metre thick.
-
Pitched Roof Slab:

Pitch roof is very common at resorts for giving the structure a countryside look. These slabs are inclined and generally covered with Tile-sheets which are extremely lightweight which further saves costs of timber or steel for support. These are recommended at places with heavy rainfall.
-
Arched Slab:
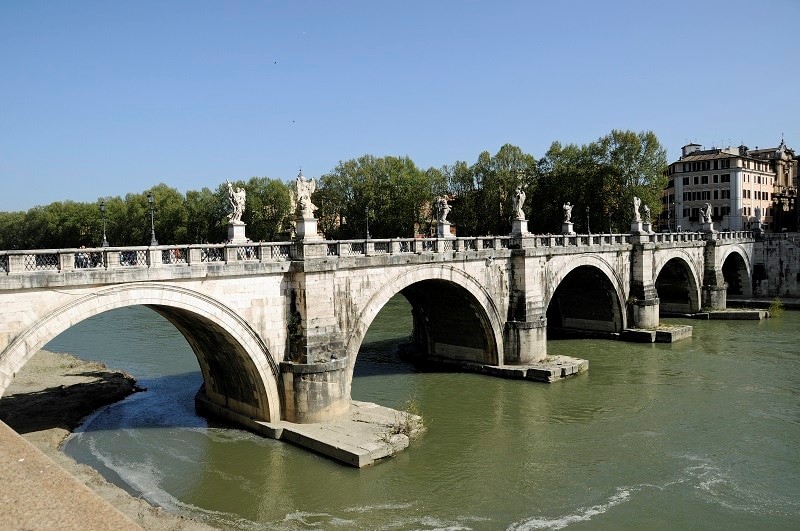

Arched slabs are used where we need to divert wind load from the structure and where there is a long curve underneath the bridge. Usually, bridges at heights are subjected to a constant moving load of vehicles and wind load. Arched slabs are proved to be very useful for such bridges.
Above all are different type of slabs can be used based on loading any requirement of structure.
Visit our ![]() Channel for more information.
Channel for more information.