What are Railway Sleepers? & Types of Sleepers Explain?
WHAT ARE RAILWAY SLEEPERS?
Railway sleepers are laying between two rail tracks to keep the correct space of the gauge. It is an important railway component. Railway sleepers ate also known as railroad ties, railway ties, or crossties.
TYPES OF SLEEPERS USED IN RAILWAYS:
There are different types of sleepers used in railways according to their suitability, availability, economy, and design.
On the basis of material used, the railway sleepers can be classified as follows:
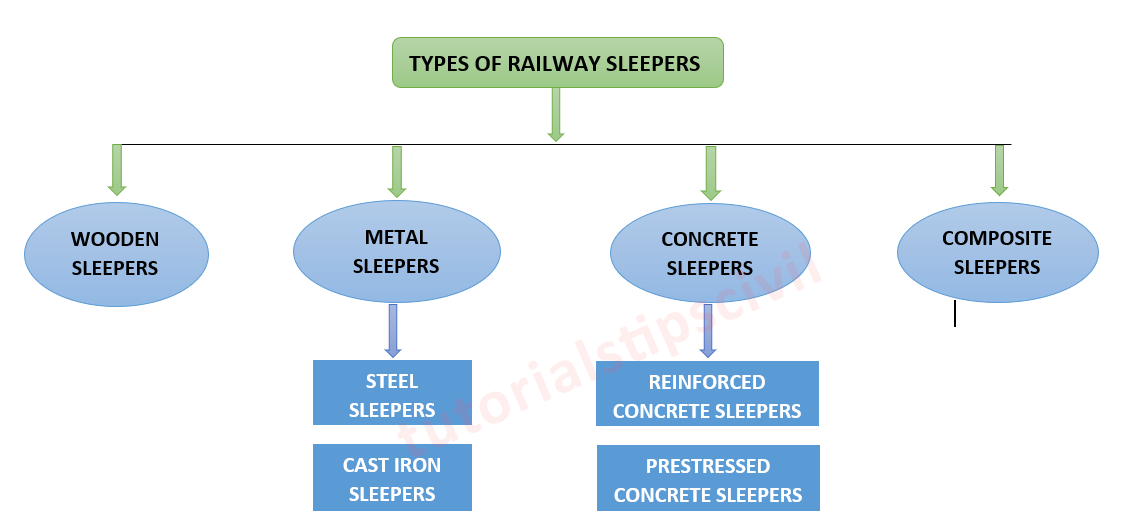
- WOODEN SLEEPERS: The sleepers use timber as a raw material to make wooden sleepers. These kinds of sleepers are using since the olden days as they fulfilled all the requirements of an ideal sleeper.
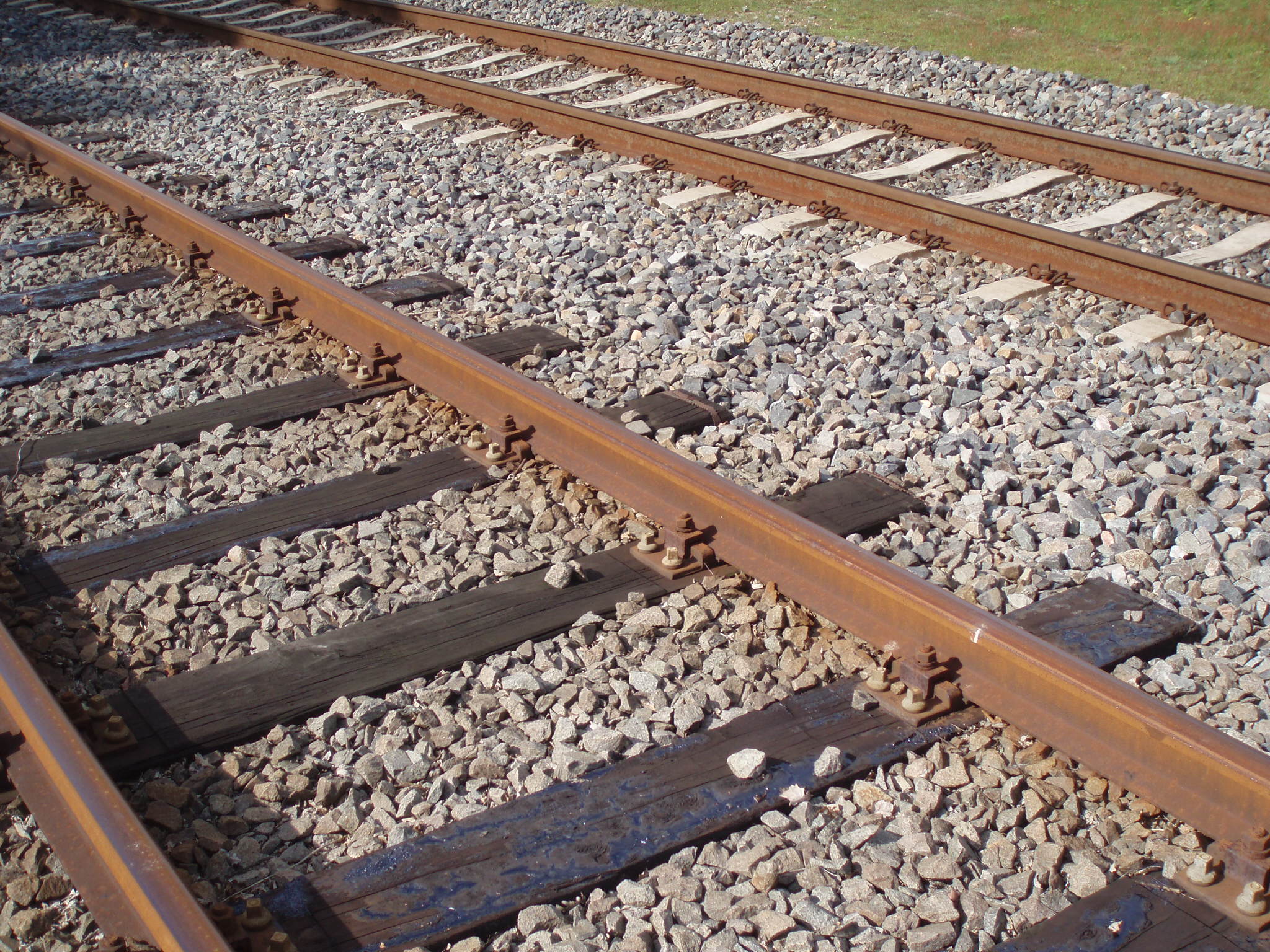

ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF WOODEN SLEEPERS
| ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES |
| The raw material is easily available. | The life span of wooden sleepers is comparatively less. |
| Manufacturing cost is comparatively low. | The scrap value is low. |
| Easy to handle and transport while installing. | Possibility of vermin attack, humidity, and fire. |
| Suitable for all kinds of ballast and chances of damage is low. | The maintenance cost is high. |
| Easy to design as it requires few fittings. | Difficult to maintain gauge of the track. |
| Absorb shocks and vibrations better than other types of sleepers. | |
| Easy to maintain or renewal. |
- METAL SLEEPERS: Sleepers usually made of steel or cast iron are known as metal sleepers. Metal sleepers are again classified into steel sleepers and cast-iron sleepers.

ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF METAL SLEEPERS
| ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES |
| The life span of metal sleepers is more and is about 35 -50 years. | Metal sleepers require more ballasts. |
| Uniform in strength and durability. | Requires more fittings which causes difficulty in maintenance. |
| The scrap value is high. | Metal is liable to rust. |
| There is no need for frequent renewal. | Changes in damages are high during accidents. |
| The gauge of the track can be easily adjusted and maintained which is economical. | Not suitable for bridges, level crossings, points, and crossings, etc. |
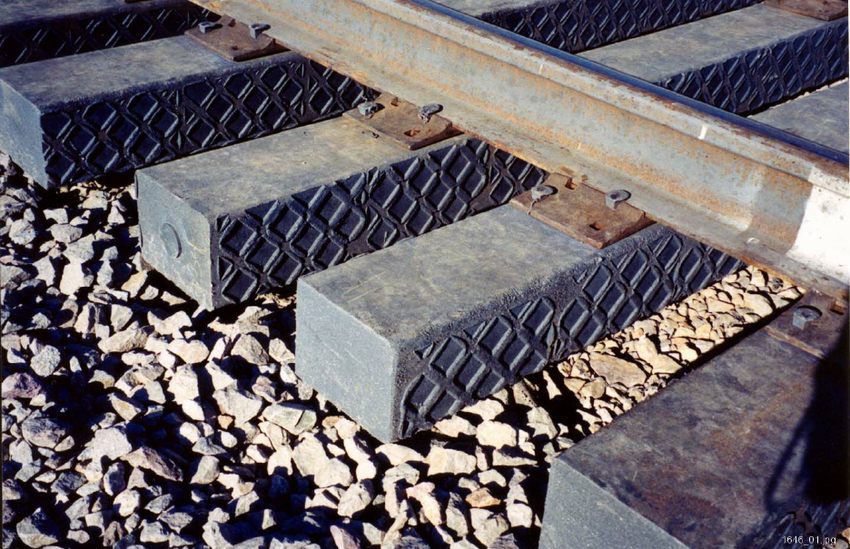
- CONCRETE SLEEPERS: The sleepers made of reinforced or prestressed cement concrete are known as concrete sleepers. These kinds of sleepers are more suitable for fast or high-speed trains. We can classify concrete sleepers into Reinforced sleepers and prestressed sleepers.

ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF CONCRETE SLEEPERS
| ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES |
| The life span of concrete sleepers is longer and s about 40-60 years. | The initial cost is high. |
| Requires few fittings | The scrap value is nil. |
| The maintenance cost is low. | Renewal is comparatively difficult. |
| More durable and suitable for circuited tracks. | Improper design and rough handling can lead to crack or break in sleepers. |
| More economical than wooden or metal sleepers. | Not suitable for tracks on bridges and at crossings. |
| Less creep in the track. | The possibility of damage is high during transportation. |
| Provide strong connections between train and sleeper. | Can not be repaired, requires replacement. |
- COMPOSITE SLEEPERS: Sleepers made of waste plastic and rubber are known as composite sleepers. It is also known as plastic sleepers.

ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF COMPOSITE SLEEPERS
| ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES |
| Eco-friendly sleepers | Resistance of composite sleepers is not good against fire. |
| Scrap value is good and contains the property of recycling. | The cost of sleepers may increase with the level of production. |
| Composite sleepers are serviceable for a longer span of 50 years. | |
| Reduces the vibration received from trains. | |
| Light-weighted with great strength. | |
| Easy to resize and can be used in any type of train section. |









