WHAT IS A RETAINING WALL?
WHAT IS A RETAINING WALL?
A retaining walls is a structure that is designed and constructed to withstand parallel pressure of soil or hold back soil materials. Traditional retaining walls are designed to resist active earth pressures or hold back soil materials only, which develops the retaining wall concept, which holds pressure. At present, this pressure could be earth filling, liquid pressure, sand, and other granular materials behind the retaining wall structure.
To design or build a wall, we consider a variety of factors like we need to understand the location and environmental factors. Building a retaining walls requires advanced planning and careful layout to avoid it becoming a hazard or collapsing.
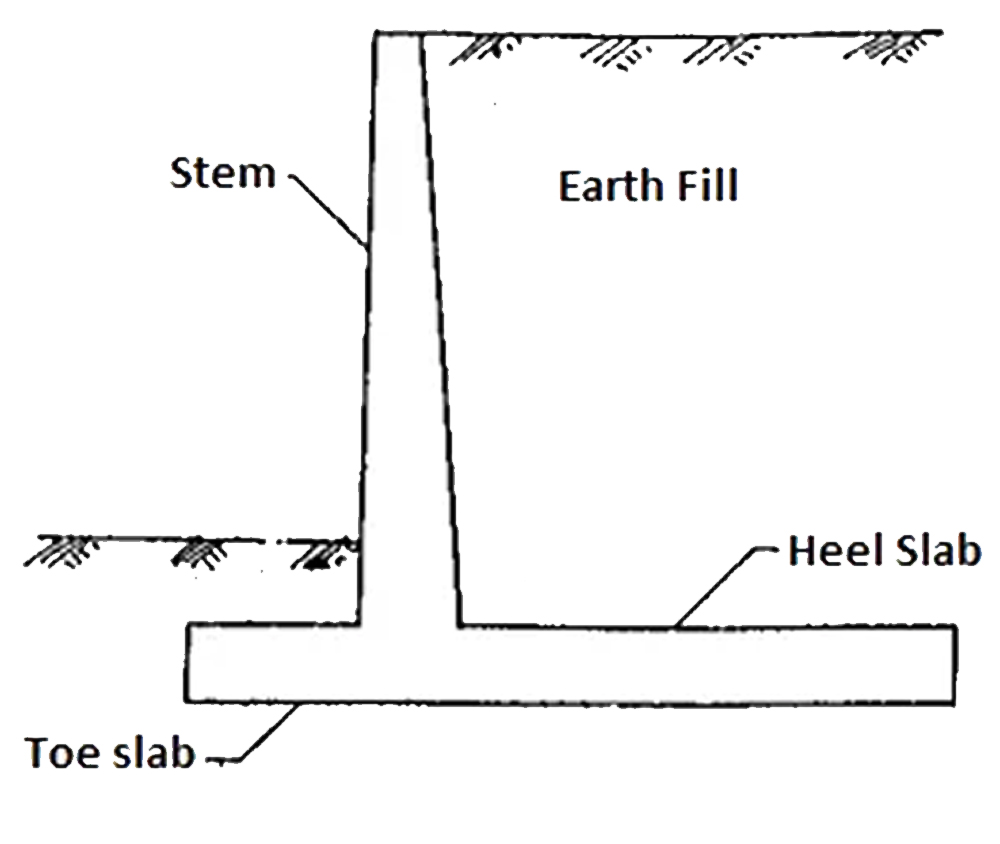
Retaining Wall Cross Section
PURPOSE OF RETAINING WALLS
Retaining walls are purposed as follows;
- Retaining walls are used to counteract as a force of gravity that holds the soil or equal pressure.
- Flatland is more desirable as compared to sloped land due to its versatility. We use retaining walls which help to convert a sloped land to flat land.
- Any construction needs elevation which requires a structured wall that can prevent soil or other material at places with sudden changes.
- It is designed to withstand the grounds or backfill, other externally exerted loads, and transmit these forces safely to a foundation.
- Access water runoff can cause soil erosion in the sloped land hence constructing a retaining wall is very helpful in preventing soil erosion and improves site drainage
- Aids in achieving certain landscape designs and improving the overall value of the property. As flat land is easy to maintain as compared to the sloped land which also reduces the maintenance cost.
- Retaining walls additionally give your landscape an aesthetically pleasing design.
APPLICATIONS OF RETAINING WALLS
- Construction of basement below ground level in buildings.
- In the bridge, work consists of the wing walls and abutment.
- To maintain slopes in hilly areas.
- As side walls of bridge approach roads.
- Providing lateral support to the embankment.
TYPES OF RETAINING WALLS
- Gravity Retaining Walls
- Crib Retaining Walls
- Gabion Retaining Walls
- Cantilever Retaining Walls
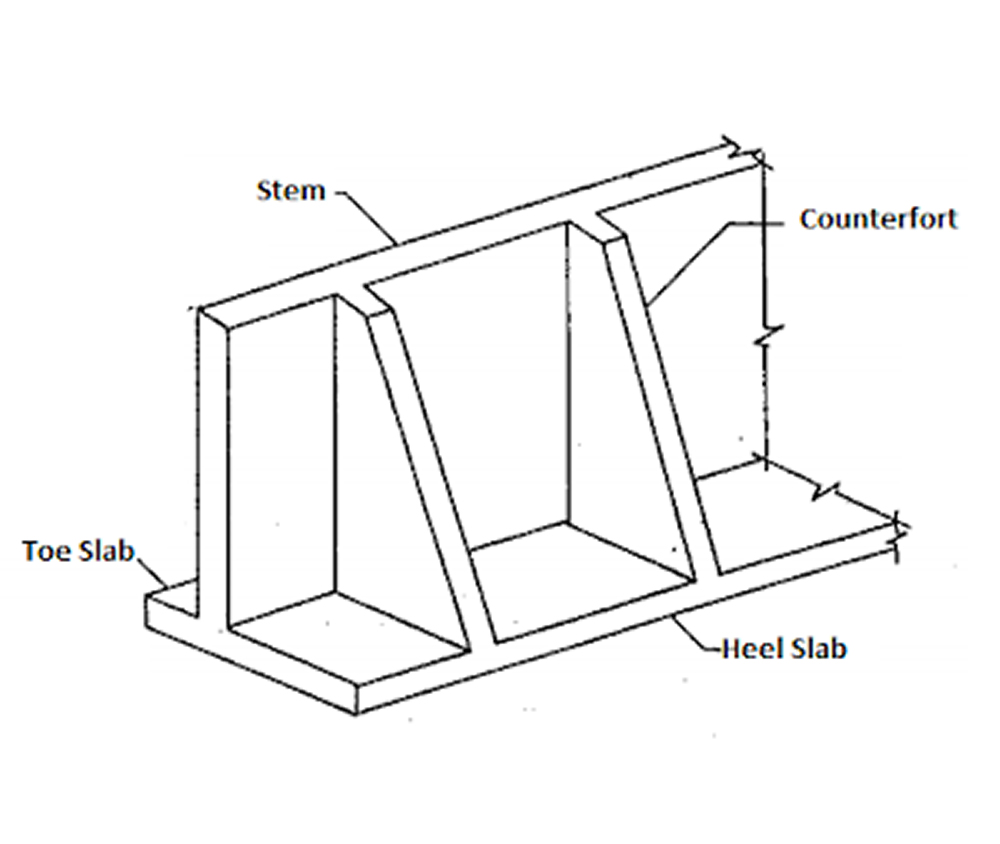
- Counter-fort / Buttressed Retaining Walls
- Anchored Retaining Walls
- Piled Retaining Walls
- Mechanically Stabilized Earth (MSE) Retaining walls
- Hybrid Systems
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |