What is Post-Tensioned Steel?
What is Post-tensioning?
Post tensioning is one of the processes of pre-stressing which is used for reinforcing cement concrete. The post-tensioning tendons (Pre-stressing steel cables) are kept inside plastic ducts or sleeves which are placed in the position before pouring concrete. As soon as the concrete has gained strength the cables are pulled tight to develop tension, and anchored against the outer ends of the concrete before the loads are applied. Post tensioning is a cast-in-situ method.
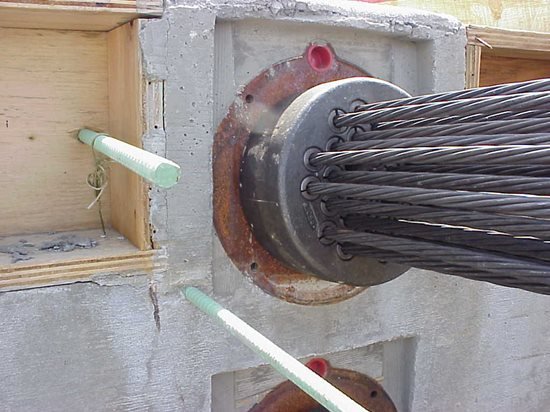
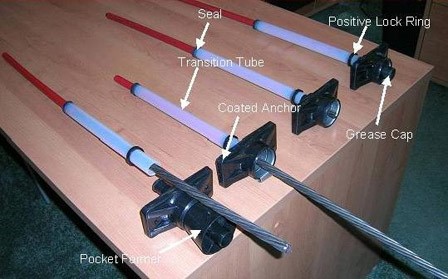
Generally, Ultra-high-strength steel strands and bars are used for post-tensioning a concrete member. For horizontal structural elements (such as beams, slabs, bridges etc.) strands are used. For vertical structural elements (such as walls, columns) bars are used. Steel strands that are used for post-tensioning have a tensile strength of 270,000 (psi), are about 0.5 inch in diameter.
Types of Post-tensioning:
1.Bonded Post-tensioning:
Bonded Post-tensioning has tendons which are permanently bonded to the concrete in vicinity by in-situ grouting of their ducts. The grouting is done to keep tendons safe from corrosion, to secure pre-tensioned tendons in place and to improve overall structure’s strength.
2. Unbonded Post-tensioning:
Unbonded Post-tensioning has tendons which are allowed to be moved longitudinally. Unlike bonded post-tensioning, casing of tendons in unbonded post-tensioning are greased properly, usually with lithium-based corrosion-inhibiting agent.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Post-tensioned Steel.
Advantages:
- Post-tensioning uses thin steel cables which helps create innovative concrete elements that are thinner, longer, and stronger than conventional RCC.
- Because elements are slender, it requires less concrete.
- It helps in reducing overall self-weight of the structure.
- Post-tensioning allows clear spans and fewer beams.
- It reduces total load coming on to the foundation.
- Beams and slabs can run continuously which is more efficient.
- Post-tensioned slabs can avoid settlement of low bearing soils.
- Post-tensioning makes complex curves or designs easier to make.
Disadvantages
- Since many tendons or steel cables are used in a Post-tensioned structure, there are high chances of corrosion,
- Skilled labour is required.
- If the post-tensioned structure is not laid as per the standards, it may cause accidents due to poor workmanship.
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————–