Introduction of Pre-engineered Building
PRE- ENGINEERED BUILDINGS (PEB)
Pre-Engineered Buildings are the building structures or components that are manufactured in the factory and assembled at the site. Usually, PEBs are steel structures because steel is the best choice for design with the feature of its elasticity and flexibility. This type of structural concept is mostly used to build Industrial Buildings, Metro Stations, Warehouses, Canopies, Bridges etc. Economically it is cheap, very fast to erect and can also be dismantled and moved to another site.
The construction speed of PEB is the fastest as compared to other constructions. While the foundation and floor slab are being constructed, the structural system – rafters (beams) and columns are fabricated in the factory. Once the foundations and plinth beam are done, the columns are shipped to the site, lifted into the place by crane and bolted together.
PURPOSE OF PRE-ENGINEERED BUILDINGS (PEB)
Pre-Engineered Building is the first preference of almost every people due to many reasons. It provides all the advantages from versatile features to long durability with the lowest maintenance costs and a faster build-up process. It also provides gigantic space which is up to 150’ wide. Their long span of time, durability, resistance to rust, fire, ad bad weather conditions are the most common and impressive features of the steel building.
COMPONENTS OF PRE-ENGINEERED BUILDINGS (PEB)
a. Main framing or vertical columns
b. End wall framing
c. Purlins, girts, and eave struts
d. Sheeting, insulation and weldmesh
e. Crane system
f. Mezzanine system
g. Paints and finishing
STEPS FOLLOWED IN THE CONSTRUCTION OF PRE-ENGINEERED BUILDINGS (PEB)
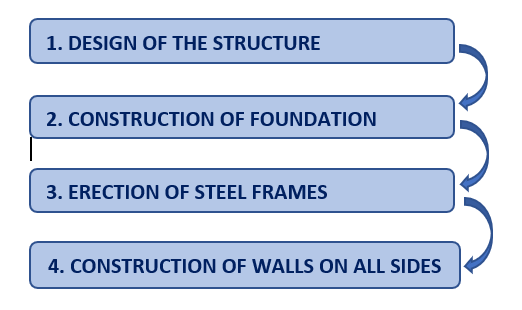
1. Design of the Structure: Design forms a key aspect in the construction of PEB. The steel frames to be used in a particular structure is extensively designed and fabricated through software in a company. This design involves the use of meticulous design software giving no room for any error or change in the structural frames.
2. Construction of Foundation: It involves the conventional construction practice of site clearance and building of concrete foundations.
Usually, shallow isolated foundations are preferred for a PEB since the self-weight of the superstructure is very less. Areas like coastal zones pile foundations are laid but the depth of the pile is less when compared to the conventional concrete structures. They often prefer to lay a flat slab base of PCC below the pedestal to prevent its direct contact with the soil. The columns of the superstructure are bolted to the pedestal.
3. Erection of Steel Frames: In the next step, the steel columns and beams are bolted together. The grade of steel used varies based on the structural requirement. For instance, if it is a one storey building then the thickness of the steel provided can be less but for a warehouse thickness to be provided increases.
4. Construction of Walls on all sides: Building the walls is the final step in the construction of a PEB. Usually, for a PEB the walls are built with a different range of materials like granite, fibre cement insulated panels, insulated steel or aluminium panels, conventional brickwork, stone cladding etc., the choice depends upon the user. Generally, an Engineer prefers insulated steel panels because of their structural stability.